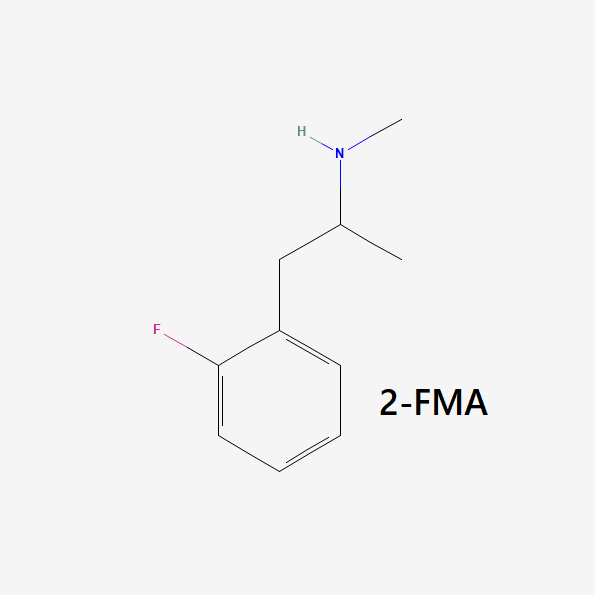
Metabolism: The only available study on the metabolism of 2-FMA indicated that N-hydroxylation and aliphatic hydroxylation are likely the characteristic metabolic pathways utilized [1].
How Does 2-FMA Work?
All of the psychoactive analogs of methamphetamine work by way of three basic mechanisms that alter the functioning of three basic neurotransmitters (dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin) as well as a host of other secondary transmitters:
- Some block the reuptake of neurotransmitters
- Some block the clearance of neurotransmitters
- Some reverse the polarity of neurotransmitter transporters
Apart from their differences in regard to these three mechanisms, amphetamine compounds express different binding affinities to the known neurotransmitters. It’s important to understand that the various ways these factors can interact play a large role in determining the effects profile of any given amphetamine.
Research that attempts to examine the precise pathways utilized by 2-FMA is lacking, but one particular study does let us know that 2-FMA has no activity at the serotonin receptors (5-HT2) [2]. This is not unheard of, but it’s not that common either: psychostimulant amphetamines tend to display stronger binding affinities in favor of either dopamine and norepinephrine or serotonin, but, in most cases, whichever receptor is not favored will still display at least some level of affinity.
Given that 2-FMA does not activate serotonin receptors, we can reasonably assume that it’s a primarily dopaminergic compound with action at the dopamine and norepinephrine receptors.
More information is needed; however, As of yet, we have no data to understand the relative levels of action at each receptor. It could be that the dopamine receptor is heavily favored or vice versa.
As it’s the most common pathway and also the one utilized by its isomers, the mechanism utilized by 2-FMA is likely reuptake inhibition. This pathway consists of inhibiting transport proteins so neurotransmitter levels outside the neuron remain elevated, which then leads to higher levels of neurotransmission. This pathway is often accompanied by the stimulation of monoamine release, a secondary pathway that induces the release of a monamine neurotransmitter from the presynaptic neuron. However, we have no solid data when it comes to 2-FMA.
What Does 2-FMA Feel Like?
With the dozens and dozens of designer drugs now on the market, it is simply too expensive for researchers to try and delve into the distinct effects profile of each NPS (New Psychoactive Substance).
For this reason, we must turn to subjective self-assessment reports found in a variety of recreational drug forums. Although this method admittedly lacks scientific objectivity, it usually produces accurate results in terms of defining the general characteristics of what a user might expect, especially when it comes to understanding how different compounds relate to each other.
The reports found online associate the use of 2-FMA with the following effects:
- Physical effects – Stimulation, Physical euphoria, Tactical enhancement, Stamina enhancement, Abnormal heartbeat, Increased heart rate, Increased blood pressure, Appetite suppression, Bronchodilation, Dehydration, Dry Mouth, Frequent urination, Increased bodily temperature, Increased perspiration, Nausea, Pupil dilation (only at higher doses), Teeth grinding, Temporary erectile dysfunction, Vasoconstriction, Restless legs
- Cognitive effects – Analysis enhancement, Anxiety & Paranoia, Cognitive euphoria, Compulsive redosing, Delusion, Disinhibition, Ego inflation, Emotion Suppression, Focus enhancement, Increased libido, Increased music appreciation, Motivation enhancement, Bodily control enhancement, Thought acceleration, Thought organization, Wakefulness, Time distortion.
- After Effects – Anxiety, Cognitive fatigue, Delusion, Depersonalization, Depression, Headaches, Irritability, Motivation suppression, Psychosis, Thought deceleration, Wakefulness
As can be seen, 2-FMA is a purely stimulant compound and produces none of the effects associated with serotonin activation. In this sense, it’s important to get a feel for the exact “texture” of its stimulant qualities. Some stimulants are often described as “chaotic,” which means they tend to overwhelm the user. On the other side of the spectrum, users often talk about “functional” or “clean” stimulants.
As a compound, 2-FMA falls squarely on the functional side, which is why it’s more popular as a productivity drug than a recreational compound, a clear indication of its functional attributes.
It’s important to note that when 2-FMA is taken in large enough quantities, the properties which enhance productivity are overwhelmed by the distracting euphoria it can produce.
When it comes to side effects, 2-FMA appears to have a more benign profile than that of other fluorinated amphetamines: it produces fewer side effects as well as “come down” effects.
Duration of Effects
One of the most popular features of 2-FMA is its long-lasting effects.
Users report that 2-FMA takes approximately 20 minutes to kick in and lasts for up to seven hours. On the other hand, the after-effects are quite short, lasting only one hour.
Is 2-FMA Safe? Risks & Side Effects
All amphetamine analogs carry a certain level of risk, especially with regard to their effects on cardiovascular health and the fact they’re mostly used as recreational drugs.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.